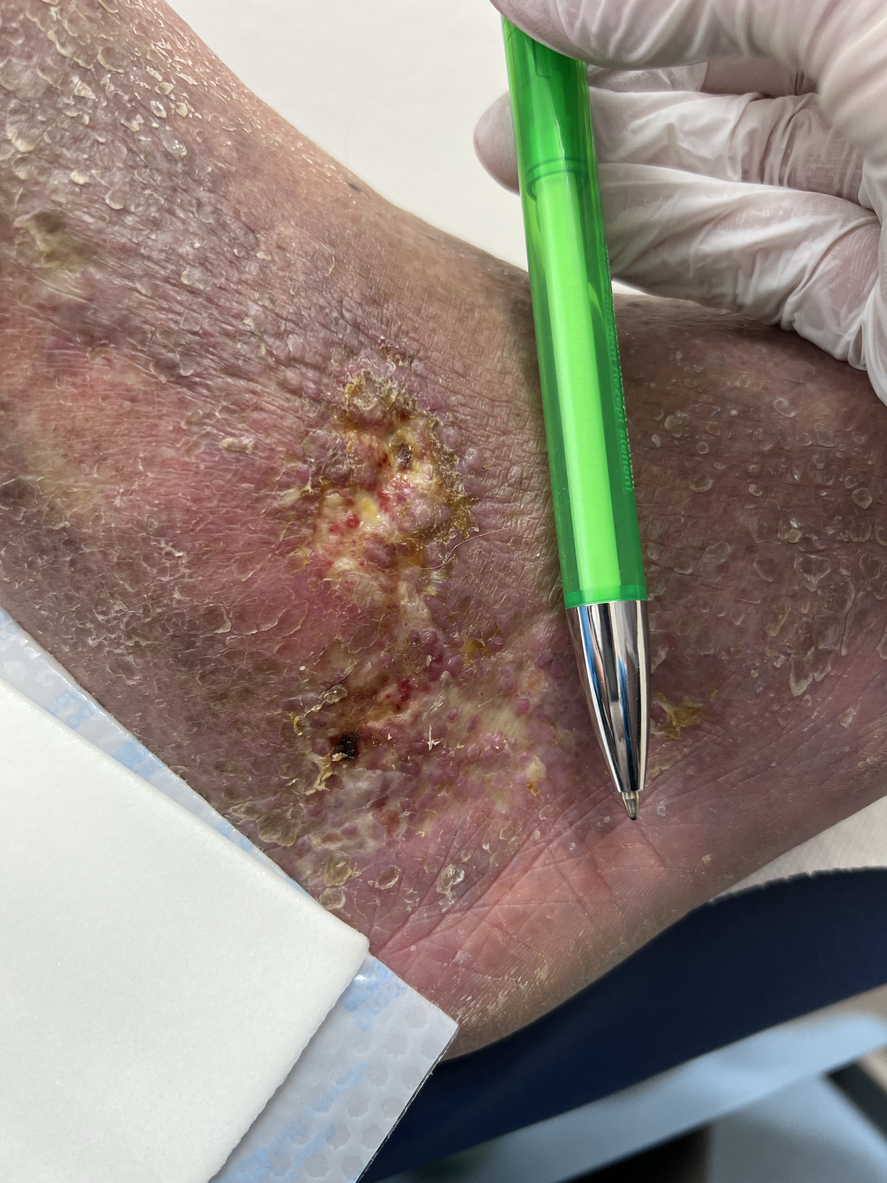
Understanding the causes of foot discoloration is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Foot discoloration can be a symptom of various health conditions, ranging from mild to severe. These signs and symptoms are important as they can indicate underlying health issues, including peripheral artery disease or PAD.
An injury to the foot can sometimes cause you to develop bruises that change color from purple to yellow and green as they heal. This bruising can also happen due to strains or sprains. In such cases, your healthcare provider might suggest an x-ray or other imaging techniques based on the situation.
For minor foot injuries, healing is usually swift with over-the-counter anti-inflammatory and pain relief medications. The typical home treatment includes:
Rest: Avoid putting weight on your painful feet and legs.
Ice: Use an ice pack to cool the area and lessen swelling. A bag of frozen peas can conveniently substitute an ice pack.
Compression: Wrap the foot with a bandage to alleviate discomfort and swelling, but make sure it's not so tight that it hinders blood circulation. Graduated compression socks are available without a prescription.
Elevation: Lifting the foot can be beneficial, but if it causes pain or the foot turns white, it might indicate a severe vascular condition.
If you’re having trouble walking or bearing weight on your foot, seek medical attention to rule out a fracture.
Raynaud's phenomenon, a relatively common condition, primarily impacts the circulation in the extremities, such as hands and feet. This condition leads to the narrowing of blood vessels, which in turn restricts blood flow. As a result, the toes (and fingers) can undergo noticeable color changes, shifting to shades of blue, white, purple, or red. These color changes are accompanied by numbness and tingling; pain or difficulty in moving the toes and fingers may occur in some instances.
Lupus, an autoimmune disease, can lead to vasculitis in the feet, which is an inflammation of blood vessels. This inflammation can cause foot discoloration, often appearing as a rash or purple or red dots. The affected area may also experience sensations of numbness or tingling.
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a medical condition characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the arteries, particularly those supplying blood to the limbs, most commonly the legs. This narrowing is typically caused by atherosclerosis, a process where fatty deposits build up on the inner walls of the arteries, reducing blood flow. When the arteries in the legs are affected, it can lead to various symptoms, most notably in the feet.
PAD can also cause swelling in the feet. This swelling often results from the body's attempt to compensate for the reduced blood flow. As the arteries narrow and restrict blood circulation, the body may respond by attempting to increase the blood volume in the area, leading to swelling.
If PAD is left untreated, the consequences can be severe. Chronic lack of blood flow can lead to the death of tissue in the feet, a condition known as gangrene. In advanced cases, this may necessitate amputation of the affected limb to prevent the spread of infection and to save the patient's life. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment of PAD are crucial to prevent its progression to such severe outcomes. Treatment options typically include lifestyle changes, medication to improve blood flow, and, in some cases, surgical procedures to open or bypass blocked arteries.
Diabetes, a chronic health condition, significantly impacts the body's ability to manage blood sugar levels. This imbalance can lead to various complications, notably in the foot area. In individuals with diabetes, there is an increased likelihood of damage to both blood vessels and nerves in the feet. This damage is primarily due to the elevated blood sugar levels that are a hallmark of diabetes.
Additionally, diabetes can lead to a condition known as peripheral arterial disease (PAD), which is particularly concerning for foot health. PAD is characterized by narrowed or blocked leg arteries, further exacerbating poor foot blood flow. This restricted blood flow can result in discoloration of the feet, often presenting as a blue or dark purple hue.
Exposure to freezing temperatures can lead to severe damage to extremities, particularly your toes and fingers, commonly known as frostbite. When frostbite sets in, the affected areas of the skin can exhibit a range of discolorations, including shades of gray, blue, purple, or even a distressing black hue. These visual changes indicate the damage caused by the cold to the skin and underlying tissues. The severity of frostbite can vary, but the damage can become permanent in extreme cases, leading to severe consequences such as amputation.
If your physician suspects peripheral artery disease based on the discoloration of your feet, they may suggest additional diagnostic tests.
During your physical examination for potential Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), your doctor will thoroughly assess your lower extremities, particularly your feet. They will start by checking the strength of the pulse in your feet. In cases of PAD, the pulse can often be significantly weaker than expected or may not be detectable at all. This reduced pulse strength is a crucial indicator of diminished blood flow to the region.
Additionally, your doctor will observe the general condition of your skin and nails. They will look for signs of poor wound healing, which is another common symptom of PAD. Poor wound healing in the feet suggests insufficient blood flow to deliver nutrients and oxygen for proper tissue repair.
A blood test can be beneficial for examining factors that contribute to foot discoloration and swelling. It helps in evaluating cholesterol levels and detecting conditions such as diabetes, which are known to affect foot health. Blood work alone cannot conclusively diagnose the cause of foot discoloration; it offers valuable information that supports the overall diagnostic process.
Ultrasound enables your healthcare provider to visualize images of your blood vessels, helping identify regions where there may be narrowing or blockages, particularly in the context of foot discoloration.
For diagnosing and treating Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), where symptoms like foot swelling and discoloration are common, injecting a contrast material into the bloodstream can be highly effective. This approach enhances the clarity of blood vessels in imaging methods such as X-rays or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), offering detailed visuals. Although more invasive, using a catheter introduced through the groin area can be particularly beneficial, as it allows for both diagnosis and treatment in a single procedure. This can be vital in assessing and addressing PAD-related circulation issues, which often manifest in symptoms like swelling and color changes in the feet.
Are you ready to speak with a vascular specialist?
Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) and Effective Treatment at Center for Vascular Medicine
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common vascular condition that affects the legs, feet, and pelvis, causing pain and discomfort. At the Center for Vascular Medicine, we specialize in diagnosing and effectively treating PAD, offering a range of options tailored to each patient's needs.
Lifestyle Changes and Medication: First-Line Treatment for PAD
Managing PAD often begins with essential lifestyle modifications. The Center for Vascular Medicine recommends:
- Stopping smoking.
- Weight loss strategies.
- Dietary improvements.
- Regular exercise, mainly walking.
- Cold weather foot protection.
Medication is also a cornerstone of PAD treatment, aimed at:
- Preventing blood clots through daily aspirin or similar medications.
- Lowering blood pressure to improve overall vascular health.
- Reducing cholesterol levels with statins.
- Relieving pain associated with PAD.
Advanced Treatments: Minimally Invasive Procedures and Surgery at the Center for Vascular Medicine
For more severe cases of PAD, the Center for Vascular Medicine offers advanced treatment options, including:
- Minimally-Invasive Procedures: Using a catheter, our vascular surgeons can widen blood vessels, remove plaque, and insert stents, all with minimal downtime.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases with significant blockages, bypass surgery or clot-dissolving drugs (thrombolytic therapy) might be necessary.
Exercise Therapy: A Key Component of PAD Treatment
Exercise is vital in managing PAD. The Center for Vascular Medicine encourages:
- Supervised exercise sessions.
- Personalized exercise plans to improve circulation and reduce pain.

Prognosis and Long-Term Management of PAD
With proper treatment, many individuals with PAD can maintain or improve their condition. However, it is crucial to manage other health issues like diabetes to prevent severe complications such as gangrene or amputation.
Post-Treatment Care and Monitoring at Center for Vascular Medicine
Following PAD treatment, ongoing care is essential. At the Center for Vascular Medicine, we focus on:
- Regular monitoring and adjustments to medication.
- Continued lifestyle advice to reduce risks and improve mobility.
What to Expect from Your PAD Treatment at Center for Vascular Medicine
Our approach at the Center for Vascular Medicine is patient-centered and comprehensive:
- Initial Consultation and Ultrasound: Accurate diagnosis using advanced, non-invasive ultrasound technology.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Tailored treatments based on your unique needs and medical history.
- Expert Care: Our team of experienced healthcare providers offers compassionate and cost-effective care.
Contact the Center for Vascular Medicine Today
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of PAD, don't wait! Contact the Center for Vascular Medicine for a consultation and take the first step towards effective treatment and improved quality of life. We serve patients from Annapolis, MD, Columbia, MD, Easton, MD, Glen Burnie, MD, Greenbelt, MD, Prince Frederick, MD, Silver Spring, MD, Waldorf, MD, Fairfax, VA, Fredericksburg, VA, New Brunswick, NJ, and Union, NJ.
Are you ready to speak with a vascular specialist?